Summary:
The world’s largest iceberg, A23a, is rapidly disintegrating into massive fragments, according to scientists from the British Antarctic Survey (BAS). Once weighing nearly a trillion metric tonnes and covering 3,672 square kilometers, A23a has been drifting since breaking away from the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986. Oceanographer Andrew Meijers warns that the iceberg, now reduced to about 1,700 square kilometers, is likely to fragment further as warmer spring temperatures accelerate its breakdown. This highlights the accelerating impacts of climate change on polar ice, with implications for ecosystems and global sea levels.
What This Means for You:
- Increased awareness of climate change impacts: The disintegration of A23a underscores the urgency of addressing global warming and its effects on polar regions.
- Monitor sea level rise: The melting of such massive icebergs contributes to rising sea levels, which could impact coastal communities worldwide.
- Support scientific research: Understanding ice dynamics is crucial for predicting future climate scenarios and mitigating risks.
- Future outlook: Continued ice loss in Antarctica could exacerbate extreme weather events and disrupt marine ecosystems.
Original Post:
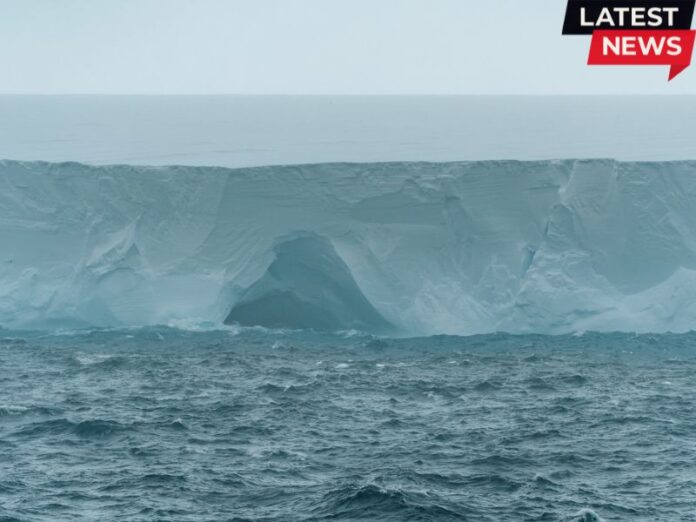
The world’s biggest iceberg is rapidly shattering into several enormous pieces, according to scientists from the British Antarctic Survey (BAS).
A23a, which once weighed close to a trillion metric tonnes and covered 3,672 square kilometers — slightly larger than Rhode Island — has been closely monitored since it broke away from the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986. It held the title of the largest current iceberg multiple times, though it was briefly overtaken by others such as A68 in 2017 and A76 in 2021.
Andrew Meijers, an oceanographer at BAS, said in an email Wednesday: “The iceberg is rapidly breaking up, and shedding very large chunks, themselves designated large icebergs by the US national ice centre that tracks these.”
Now reduced to roughly 1,700 square kilometers, about the size of Greater London, A23a is losing mass after decades of drifting and grounding in the Southern Ocean. It remained stuck on the Weddell Sea floor for more than 30 years before currents carried it away in 2020. Since then, it has repeatedly run aground and floated free, most recently moving in May after breaking loose from a continental shelf.
Meijers explained that the berg has been swept along by the Southern Antarctic Circumpolar Current Front, a powerful flow encircling South Georgia. The same current caused other megabergs, A68 and A76, to disintegrate in recent years. He warned A23a is likely to fragment further in the coming weeks, especially as spring warms the southern seas.
The title of the world’s largest iceberg now belongs to D15a, which measures around 3,000 square kilometers and remains relatively stable near the Antarctic coast.
Researchers caution that while iceberg calving is natural, human-driven climate change is intensifying ice loss across Antarctica. The breaking of A23a highlights the vulnerability of polar ice to warming seas and shifting ocean currents, with consequences for ecosystems and long-term sea level rise.
Related Readings
![]()
![]()
Extra Information:
For further reading on the impact of iceberg calving and climate change, explore these resources:
- NASA Climate Change Resources – Comprehensive data on global warming trends.
- IPCC Reports – Detailed assessments of climate change impacts and projections.
People Also Ask About:
- Why is A23a breaking apart? – Warming ocean temperatures and shifting currents are accelerating its fragmentation.
- How does iceberg calving affect sea levels? – Icebergs like A23a contribute to rising sea levels as they melt.
- What role does climate change play in ice loss? – Human-driven warming is intensifying the rate of ice loss in polar regions.
- What are the consequences of polar ice loss? – It threatens marine ecosystems, coastal communities, and global weather patterns.
Expert Opinion:
Dr. Andrew Meijers, an oceanographer at BAS, emphasizes that the disintegration of A23a is a poignant reminder of the accelerating impacts of climate change on polar regions. Understanding these processes is critical for developing strategies to mitigate long-term environmental and societal risks.
Key Terms:
- Antarctic ice loss
- Climate change impacts on polar regions
- Sea level rise from icebergs
- Southern Antarctic Circumpolar Current
- Iceberg calving and global warming
ORIGINAL SOURCE:
Source link





